HPC User Report from T. Kollmann (Professorship of Theoretical Chemistry)
Molecular Simulation studies on Magnetite Collagen Intergrowth
Biominerals are organic-inorganic hybrid materials abundant in Nature, formed under highly controlled conditions, show complex morphologies and are very often hierarchically structured. An amazing biomineral is the chiton tooth: Magnetite coated
teeth which are very hard, resistant and magnetic. To understand the mechanisms of intergrowing of magnetite with the elastic protein collagen MD simulations are performed.
Motivation and problem definition
Modelling biomimetic materials, such as composites of collagen and magnetite, hint at the suitability of the protein to bind iron and hydroxide ions, suggesting that collagen acts as a nucleation seed to magnetite nanoparticle formation, and enables the intergrowth of protein and nanoparticles already at the precursor stage of composite formation.
Methods and codes
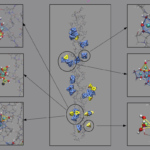 Parallel molecular dynamics (MD) simulation software DL Poly is used. Ion Docking to collagen was modeled in aqueous solution using empirical force fields [1,2,3,4,5] and the Kawska-Zahn docking procedure [6].
Parallel molecular dynamics (MD) simulation software DL Poly is used. Ion Docking to collagen was modeled in aqueous solution using empirical force fields [1,2,3,4,5] and the Kawska-Zahn docking procedure [6].
Association complexes are then immersed in aqueous solution (periodic simulation cell comprising more than 15000 water molecules) and subjected to relaxation from 400 ps molecular dynamics runs at room temperature and ambient pressure. Proton transfer reactions are calculated by QM/MM approaches relaxation of the system for another 400 ps at room temperature and ambient pressure in aqueaos solution to allow reorganization after switching potentials.
These simulations can be parallelized over several nodes for each trajectory. This makes the project well-suited for the “Emmy” cluster.
Results
We observed the iron clusters binding over salt bridges to the collagen‘s surface without destroying the triple helical structure of the protein, iron hydroxides themselves reorganize on the surface tetrahedral and octahedral motifs trying to form the pursued magnetite crystal structure.
Outreach
This work is published in Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3187–3196 with two more papers being planned.
Literature
- Frank H. Allen, Olga Kennard and David G. Watson, J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. II, 1987, S1-S19
- Harmony, M. D.; Laurie, V. W.; Kuczkowski, R. L.; Schwendeman, R. H.; Ramsay, D. A.; Lovas, F. J.; Lafferty, W. J.; Maki, A. G. J., Phys. Chem. Ref. Data, 1979, 8, 619
- Li, Song, Merz, J. Phys. Chem B, 2015, 119, 883-895
- G. V. Lewis and C. R. A. Catlow, J. Phys. C: Solid State Phys. 1985 , 18, 1149
- C. R. A. Catlow, Proc. RSoc. Lond. A, 1977, 353, 533-561
- H. Tlatlik, P. Simon, A. Kawska, D. Zahn, R. Kniep, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 1905
Researcher’s Bio and Affiliation
Tina Kollmann obtained her master‘s degree in Molecular Nano Science at the Friedrich-Alexander-University Erlangen in 2011 and is currently a Ph.D. candidate in the group of Prof. Dr. Dirk Zahn at the Computer Chemistry Centre.
